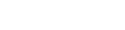Shipping Market Outlook – End Q3 2023 Forecast Values
Overview
High energy prices and aggressive interest rate hikes will lead to slow economic growth in western economies which could potentially spread to Asia. High inflation and monetary measures to combat the higher prices will likely impact consumer sentiment and investment spending. Tight monetary policy aimed at cooling down economies may also hamper investment appetite due to lower liquidity and higher credit risk. It is difficult to predict any potential escalation or de-escalation in the Russia-Ukraine conflict, and the duration and ramifications of sanctions and embargoes are uncertain.
Tankers
While Russian exports for both crude oil and products will decline, sourcing supplies to Europe from other suppliers such as MEG, US, Latin America, should increase tonne-mile demand and support Tanker rates going forward.
Although Tanker newbuilding activity has picked up, ordering has been low for the past two years, which with expectations of a slight increase in scrapping activity serves well for the overall market balance. The orderbook remains low at 5% of the total fleet, having increased slightly during Q3.
The International Maritime Organisation’s (IMO) greenhouse gas (GHG) emission targets that were enforced in 2023 should have an impact on fleet efficiency. This will have implications for the effective trading capacity of the fleet, boosting prospects from 2023/2024 onwards.
Tonne-mile demand expectations for 2023 and beyond remain strong in our current base case, assuming that oil demand is not severely impacted by high oil prices and inflation in the Western economies. And, with the reversal of its strict zero Covid policy, China is expected to reclaim its position as the leading oil demand driver, supporting Tanker markets further.
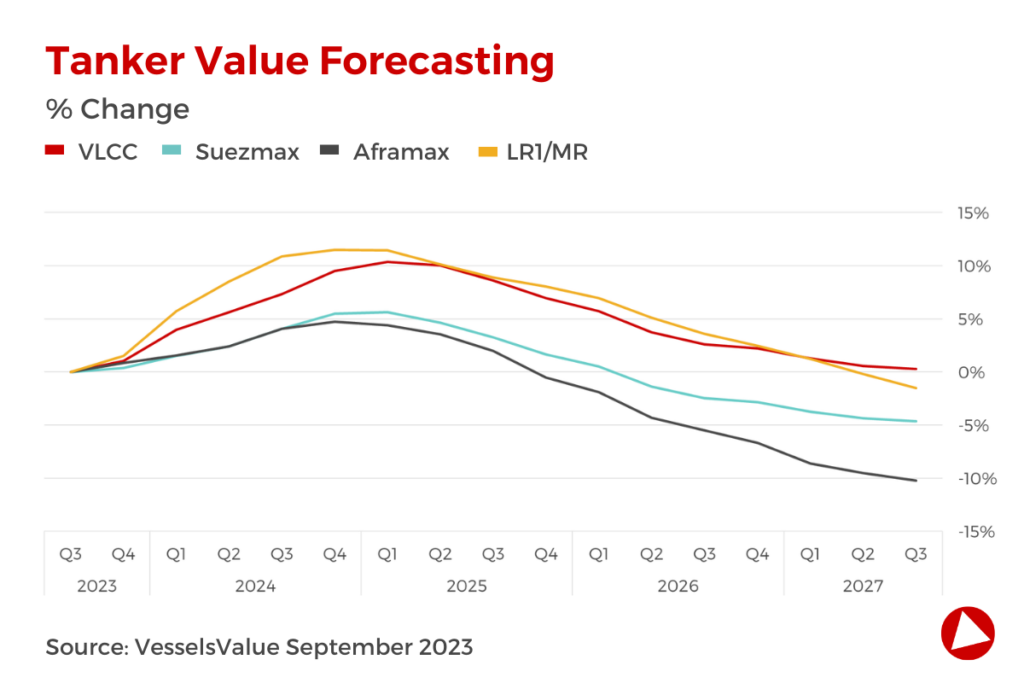
Bulkers
Despite some near-term adjustments, the outlook for Bulkers is overall positive going forward. Fleet growth is expected to be outpaced by demand which will tighten the market balance.
Following a year of decline in China’s real estate sector, the latest government strategy lays the foundation for a more consistent and sustainable path of growth. This bodes well for the iron ore trade which should receive additional support due to historically inventory levels which could encourage increased stock piling.
India is a country in a period of rapid growth with an expected average GDP growth of 6.5% per year during 2023-2026, and it will be a key driver for growth in seaborne trade.
The Bauxite trade has made headlines this quarter as Indonesia’s export ban led to China increasing imports from Guinea. This is positive news for Bulkers due to increased tonne mile demand and this also has the potential to alter the seasonal patterns, particularly for Capesize vessels heavily involved in the iron ore and bauxite trades.
Although high inflation and increasing interest rates in the West have hampered economic growth in the short term. Looking further ahead, a recovery in western economies and investment into green energy infrastructure could be positive for Bulker demand.
The dry bulk supply fundamentals remain favourable to owners. Uncertainty about the future of fuels and high newbuilding prices have made owners reluctant to order new vessels, which has led to a low order book to fleet ratio of 8%.
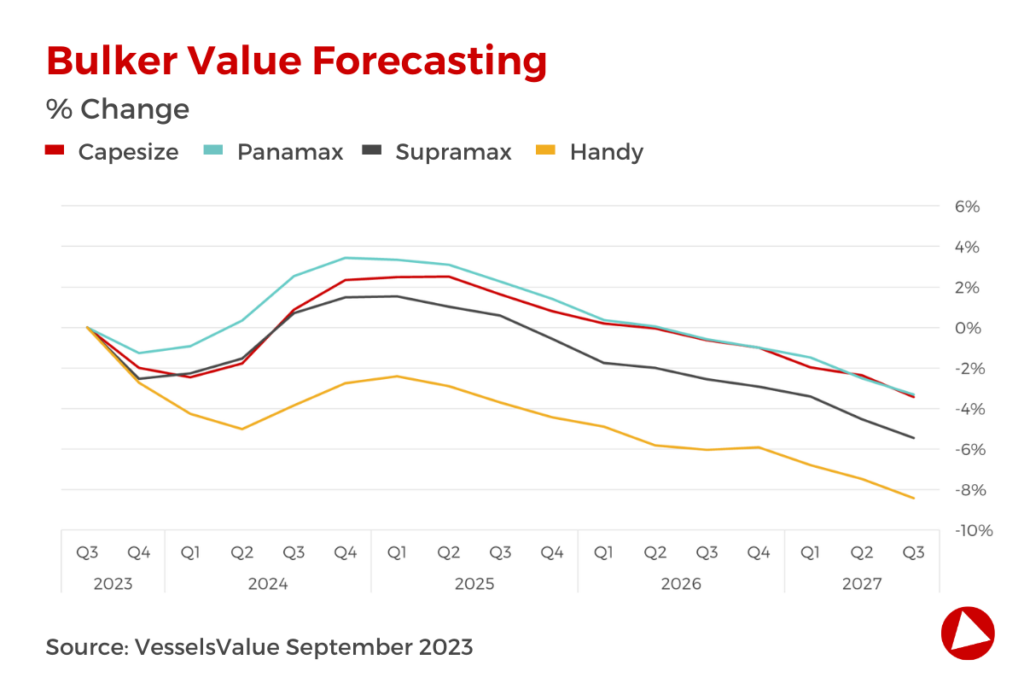
Containers
Our current analysis points to a demand growth of around 2.2% yearly average over the period 2023-2026, with a forecasted reduction in growth for 2023 of -2.2%, following -5.2% in 2022.
In conjunction with easing congestion, rates have come down sharply and are expected to bottom out in 2H24 before rising somewhat as the pains of returning to normal abate. The actual supply growth was recorded at 2.3% in 2022 which we expect will rise to 5.6% in 2023.
Looking at the orderbook, dual fuel vessels have surpassed 50% in terms of TEU, indicating that liners are well underway in the green transition.
The orderbook is still significant at 31.4% of the fleet at the beginning of July. However, reports indicate that shipyards are experiencing delays, which on one hand can postpone the delivery schedule and on the other hand further delay scrapping activity.
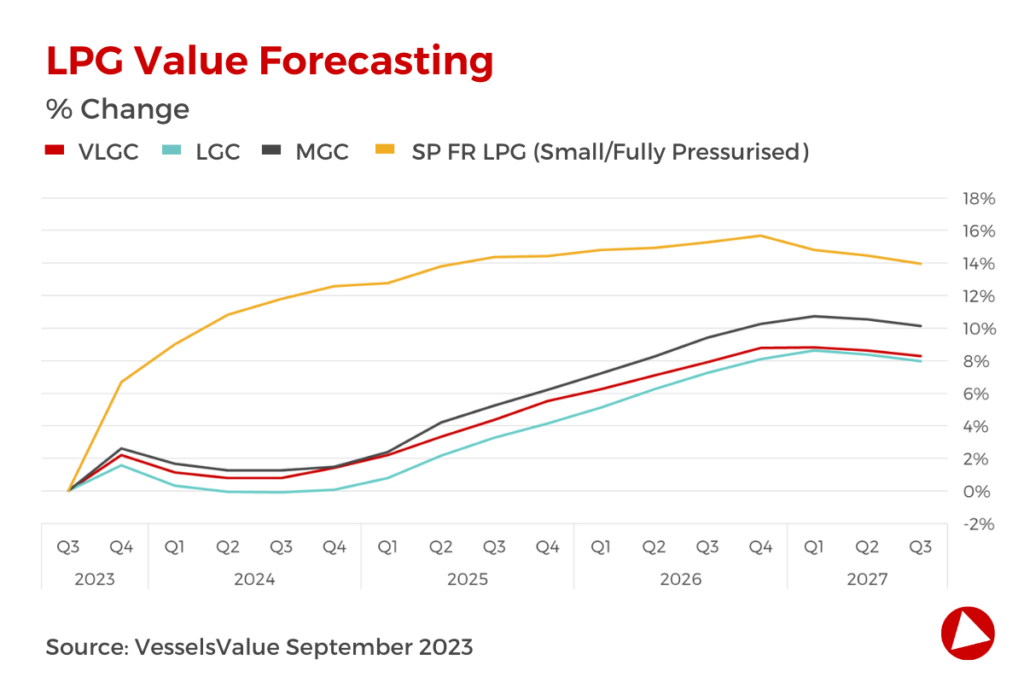
Gas
We expect the supply side in the VLGC segment to outgrow the demand side in the last quarter of 2023. Increased inefficiencies driven by new regulations aiming to reduce the greenhouse gases from shipping, are likely to soften the downfall as well as a substantially high arbitrage.
Earnings are forecasted to decrease in Q4-2023 and fall further in 2024 as US production growth is expected to be modest.
The stress on transits through the Panama Canal is likely to see large seasonal variations, with the recent drought in the Gatun Lakes as something that could substantially impact the VLGC transits.
Asian demand for LPG is forecasted to see slight growth in the last quarter of 2023 for PDH plants and domestic consumption, as economic growth is moderate.
We forecast a continuation of current trade pattern in the ammonia market. By 2026 we are likely to see the beginning of moderate volumes of blue ammonia.
Want to know more about how our
data can help you assess the market?